In recent years, more and more new automotive electronic products such as sensors and chips have been introduced into the automotive industry, and the automotive standards have also become chaotic. Satisfy, conform, achieve The streets are filled with start-up companies, with a dizzying adjective added before the word "car specification level", and naturally there are also companies with the word "mass production" added after the word "car specification level".
At present, the AEQ quality standard is one of the most relevant standards for automotive electronics in the automotive industry. AEC-Q100 is a failure mechanism based on stress testing of packaged integrated circuits. The purpose of the Automotive Electronics Committee (AEC) is to establish common component qualifications and quality system standards. The current application of AEC-Q100 in integrated circuits is mainly focused on discrete components AEC-Q101 and passive components AEC-Q200. AEC-Q100 is divided into five levels based on temperature range as the fundamental classification criterion. Among them, level 0 is the highest (-40 ° C to+150 ° C), level 1 is -40 ° C to+125 ° C, level 2 is -40 ° C to+105 ° C (which is relatively common), and the lowest level is level 4 (0 ° C to+70 ° C). Level 0 is mainly used under the engine hood for the worst environmental conditions, while levels 1 and 2 are used in other parts of the car.
In addition to AEQ, another specification that needs to be followed is ISO 26262 developed by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), mainly used for functional safety components such as ADAS related sensors and systems.
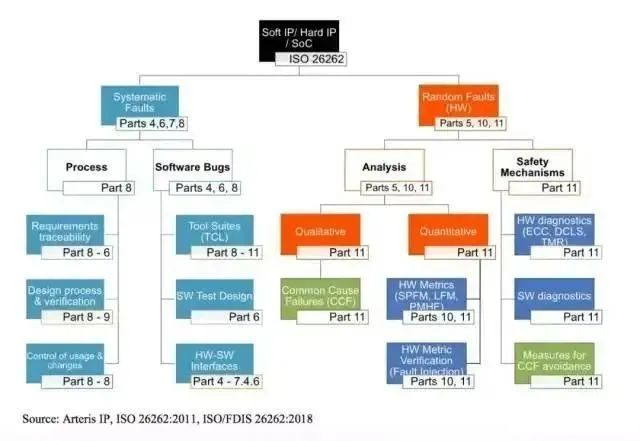
Automotive Safety Integrity Level (ASIL) is a risk classification scheme defined by ISO 26262- Road Vehicle Functional Safety Standard. This is an adjustment to the safety integrity level used in the automotive industry in IEC 61508. This classification helps to define the safety requirements necessary to comply with the ISO 26262 standard. ASIL is a risk analysis that targets potential hazards by observing the severity, exposure level, and controllability of the driving scenario of a car. This hazard safety objective also complies with ASIL regulations. ASIL A, ASIL B, ASIL C, and ASIL D are four levels, with ASIL D having the highest requirement for product integrity and ASIL A having the lowest.
ASILs are established through hazard analysis and risk assessment. For each electronic component in a car, engineers must measure three specific variables: severity and exposure, controllability, all of which are decomposed into subclasses.
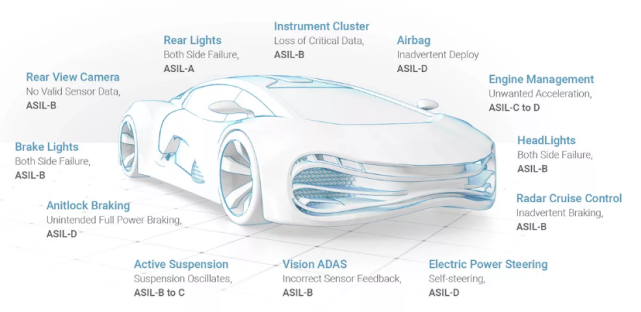
Considering the speculative work involved in determining the ASIL hazard level, the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) drafted J2980, "Factors to Consider ISO 26262 ASIL Hazard Levels," in 2015. These guidelines provide clear guidelines for evaluating specific levels of exposure, severity, controllability, and other aspects of hazards.
ISO 26262 has become a guiding standard for functional safety in the automotive development process. The chip (microcontroller) was first used in cars to control the operation of the engine. It is called an ECU or engine control unit. Up to now, there are over 50 ECUs in cars dedicated to monitoring various aspects such as power systems, in car entertainment systems, active safety systems, and communication systems. Next, in addition to distributed networks and centralized domain control architectures, more chips (more complex than previous ECUs) will also appear in the new car.
With the increasingly fierce competition in the global automotive industry, domestic automotive chip manufacturers have improved the technological level and market competitiveness of domestic automotive chips by introducing advanced technology and management experience, promoting the rapid development of the domestic automotive chip industry. At the same time, facing competition and challenges in the international market, domestic automotive chip manufacturers need to constantly innovate and progress, strengthen cooperation and communication with international peers, and promote the healthy development of the domestic automotive chip industry.
This article is reprinted from the internet. If there is any infringement, please contact us to delete it. Thank you!


















